Understanding Anger
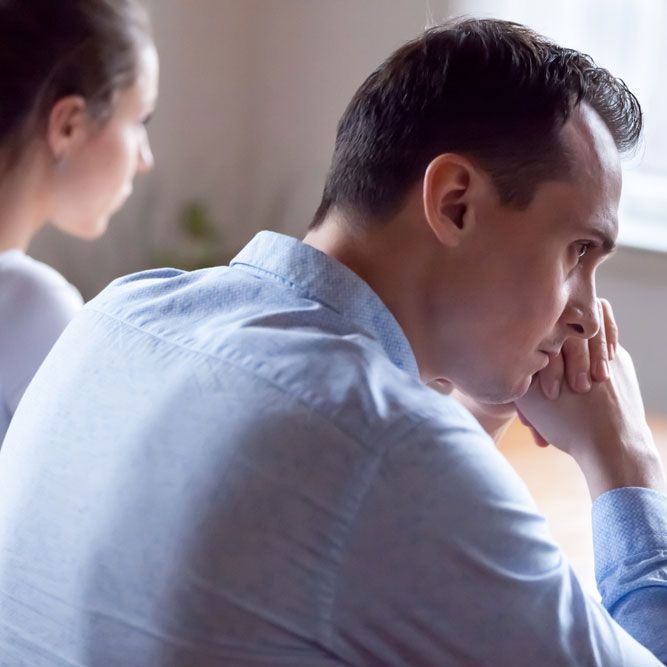
Controlling anger begins with gaining an understanding of this emotion. Anger is a part of being human and arises when we feel threatened, frustrated, or treated unfairly. Its intensity can vary from annoyance to fury and it often involves physical, mental and behavioral reactions. Effectively managing anger requires delving into its root causes and triggers to gain insights into how to handle this emotion. In this blog, you can learn root causes of anger, anger issue symptoms, and strategies to control the anger.
Root Causes of Anger
Anger is an emotion that can arise due to various underlying factors. It is crucial to understand the root causes of anger in order to effectively manage and address this feeling so that you can control the anger. Here are some common triggers of anger so that you can ultimately learn how to control your anger:
- Frustration: Anger often stems from feelings of frustration when we encounter obstacles, challenges or barriers that hinder us from achieving our goals. The sense of being stuck or blocked can gradually build up and lead to an outburst of anger as a response to these perceived roadblocks.
- Perceived Threats: Anger can also be a reaction when we perceive physical or emotional threats. When we feel unsafe or believe our well being is at risk our natural instinct may be to respond with anger as a mechanism.
- Injustice: Witnessing or experiencing unfairness, discrimination, or mistreatment can elicit feelings of anger and indignation. The sense of outrage over such injustices can intensify the anger response compelling individuals to speak out against them or take action in response to perceived wrongdoings.
- Unmet Expectations: When our expectations are not met, in relationships or work situations, it can evoke feelings of anger and disappointment. Whether its promises left unfulfilled, needs unmet, or illusions shattered, the difference between what we anticipated and what actually happens can make it difficult to control the anger.
- Feeling Disrespected: Experiencing disrespect or being made to feel small can be a source of anger. When we perceive that our worth or dignity is being undermined it can lead to feelings of outrage and anger as we strive to protect our self esteem and demand respect.
- Control Issues: People often experience anger when they believe they have control over their situation or surroundings. This sense of helplessness or powerlessness can lead to frustration and anger as individuals try to regain a sense of control in their lives.
- Pent-Up Emotions: Emotions that are suppressed or left unexpressed such as sadness, fear, or hurt can gradually, eventually manifest as anger. Anger may serve as a way to conceal or cope with vulnerable emotions that we hesitate to confront directly. Although concealed, it does not mean the anger is controlled in a healthy manner.
- Stress and Overwhelm: High levels of stress and feeling overwhelmed can intensify our state, making us more prone to angry reactions. As stress builds up it can diminish our ability to handle frustrations and challenges effectively, leading us to experience outbursts of anger, unable to control the anger
Physical Response to Anger
Anger can trigger an intense physical response known as the “fight or flight” reaction. When we perceive a threat, our body automatically prepares itself to either defend or escape from the situation. This innate response has evolved over time to help us survive in circumstances. However, in today’s world, this reaction can sometimes be triggered in situations that are not life threatening, resulting in an angry outburst. Some anger issue symptoms include:
- Increased Heart Rate: When we become angry our body releases stress hormones like adrenaline and noradrenaline causing our heart rate to rise rapidly. This increased heart rate ensures that more blood is pumped to our muscles preparing them for action.
- Tense Muscles: Anger also leads to muscle tension as part of the fight or flight response. Muscles in areas such as the shoulders, neck and jaw become tense as our body readies itself for reactions.
- Elevated Blood Pressure: The release of stress hormones causes blood vessels to constrict resulting in blood pressure levels. This response aims to provide oxygen to vital organs and support physical readiness.
- Rapid Breathing: When our bodies need oxygen we tend to breathe faster and not as deeply. This helps us prepare for any activity that might be required during the fight or flight response.
- Sweating: Anger can cause sweating as our bodies try to cool down during times of heightened arousal.
- Pupil Dilation: The pupils of the eyes dilate, allowing more light to enter, which improves visual acuity and enhances the ability to perceive threats.
Cognitive Appraisal
Cognitive appraisal refers to the way we interpret and evaluate a situation or event, which influences our emotional response to it. In the context of how to control your anger, cognitive appraisal plays a significant role in determining the intensity of our emotional reaction. How we perceive and interpret a situation can either escalate or diminish feelings of anger.
- Primary Appraisal: This is the initial evaluation of a situation. We assess whether an event or action is positive, negative, or neutral. If we perceive the situation as threatening, frustrating, or unjust, it can trigger anger.
- Secondary Appraisal: After the primary appraisal, we evaluate our ability to cope with the situation. If we believe we have the resources to deal with the perceived threat or injustice, we might feel less angry. On the other hand, if we feel incapable of coping, we may be unable to control the anger.
- Cognitive Distortions: Our cognitive appraisal can be influenced by cognitive distortions, which are irrational and exaggerated thought patterns. Engaging in cognitive distortions make it harder to control the anger, and can prolong anger issue signs and symptoms. Common cognitive distortions associated with anger include:
- All-or-Nothing Thinking: Seeing situations as black or white, without acknowledging shades of gray.
- Jumping to Conclusions: Assuming negative intentions or outcomes without evidence.
- Magnification: Exaggerating the importance or impact of a situation.
- Personalization: Assuming responsibility for events beyond our control.
- Attribution Style: Our attribution style refers to how we assign causes to events or actions. Individuals with an aggressive attribution style may interpret others’ actions as intentional, leading to heightened anger.
Strategies to Control Anger
While anger is a natural emotion, it is essential to learn how to control your anger to prevent negative consequences for ourselves and others. Here are some effective strategies to control anger:
- Recognize Early Signs: Pay attention to the physical signs and early emotional cues of anger, such as tension in the body, increased heart rate, or feelings of irritation. Recognizing these anger issue signs allow you to control the anger and intervene before anger escalates.
- Practice Deep Breathing: When anger issue signs surface, take slow, deep breaths to activate the body’s relaxation response. Focus on the breath to calm the mind and body, allowing for more rational thinking.
- Use “I” Statements: When communicating your feelings of anger, use “I” statements to express your emotions without blaming others. This helps avoid escalating conflicts, encourages healthy communication, and learns how to control the anger.
- Take a Timeout: If you feel overwhelmed by anger, step away from the situation temporarily. Find a quiet space to collect your thoughts and emotions before addressing the issue.
- Practice Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness through activities like meditation or deep contemplation can enhance our self awareness and emotional control. By being engaged in the present moment we can effectively respond to various situations, with a calm and rational mindset, and control the anger.
- Seek Support: Share your feelings with a trusted friend, family member, or mental health professional. Venting to someone who listens without judgment can provide relief and help you gain perspective on the situation.
- Identify Triggers and Patterns: Reflect on common triggers and patterns that lead to anger episodes. This self-awareness can help you avoid or manage situations that frequently elicit anger issue symptoms.
- Engage in Physical Activity: Engaging in physical exercise is a great way to alleviate accumulated tension and minimize stress levels. It can effectively regulate emotions and contribute to an enhanced sense of well being.
- Practice Assertiveness: You can develop the skill of expressing yourself in a confident and respectful manner, which allows for clear communication of personal needs and boundaries without relying on anger or aggression.
- Seek Professional Help: If you find it challenging to control anger or if it is negatively impacting your life and relationships, consider seeking professional help from mental health services like Uncover Mental Health Counseling.
Control the anger today!
Understanding anger and adopting effective strategies to manage it are essential for maintaining emotional well-being and healthy relationships. By recognizing early signs of anger, practicing relaxation techniques, and seeking support when needed, individuals can navigate challenging situations with greater composure and resilience. Remember that controlling anger is a skill that can be developed with practice and patience. In cases where anger becomes overwhelming or persistent, seeking professional help at Uncover Mental Health Counseling can provide valuable support and guidance in addressing anger-related issues. Taking proactive steps to manage anger will lead to a more balanced and fulfilling life for yourself and those around you.