Navigating the world with low functioning autism can feel like sailing through stormy seas, with challenges looming at every turn. It’s a journey marked by significant hurdles, from communication struggles to sensory sensitivities and social complexities. In this blog, we’ll explore the intricacies of low functioning autism, shedding light on its challenges, distinctions, and the vital support it demands.
What is Low Functioning Autism?
Low functioning autism is a term used to describe individuals on the autism spectrum who require significant support in various aspects of daily life, including communication, social interaction, and coping with sensory stimuli. Autism, including its low functioning variant, is a spectrum disorder, which means it manifests differently in each individual.
For those with low functioning autism, navigating the world can be particularly challenging due to difficulties in communication, social interaction, and behavior regulation. These individuals often require substantial assistance and specialized interventions to manage daily tasks and engage with others effectively. It’s important to understand that low functioning autism does not define a person’s worth or potential, but rather reflects the level of support they need to thrive.
Signs of Low Functioning Autism
Now, let’s take a closer look at some common signs of low functioning autism:
- Limited Communication Skills: Individuals with low functioning autism may struggle to express their needs or thoughts verbally or non-verbally. They may have difficulty understanding language or using it to communicate effectively.
- Social Challenges: Social interaction can be particularly challenging for individuals with low functioning autism. They may have difficulty understanding social cues, making eye contact, or forming and maintaining friendships. As a result, they may appear socially isolated or withdrawn.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Engaging in repetitive movements or actions, such as hand-flapping, rocking, or spinning objects, is common among individuals with low functioning autism. These repetitive behaviors may serve as a way to self-soothe or cope with sensory overload.
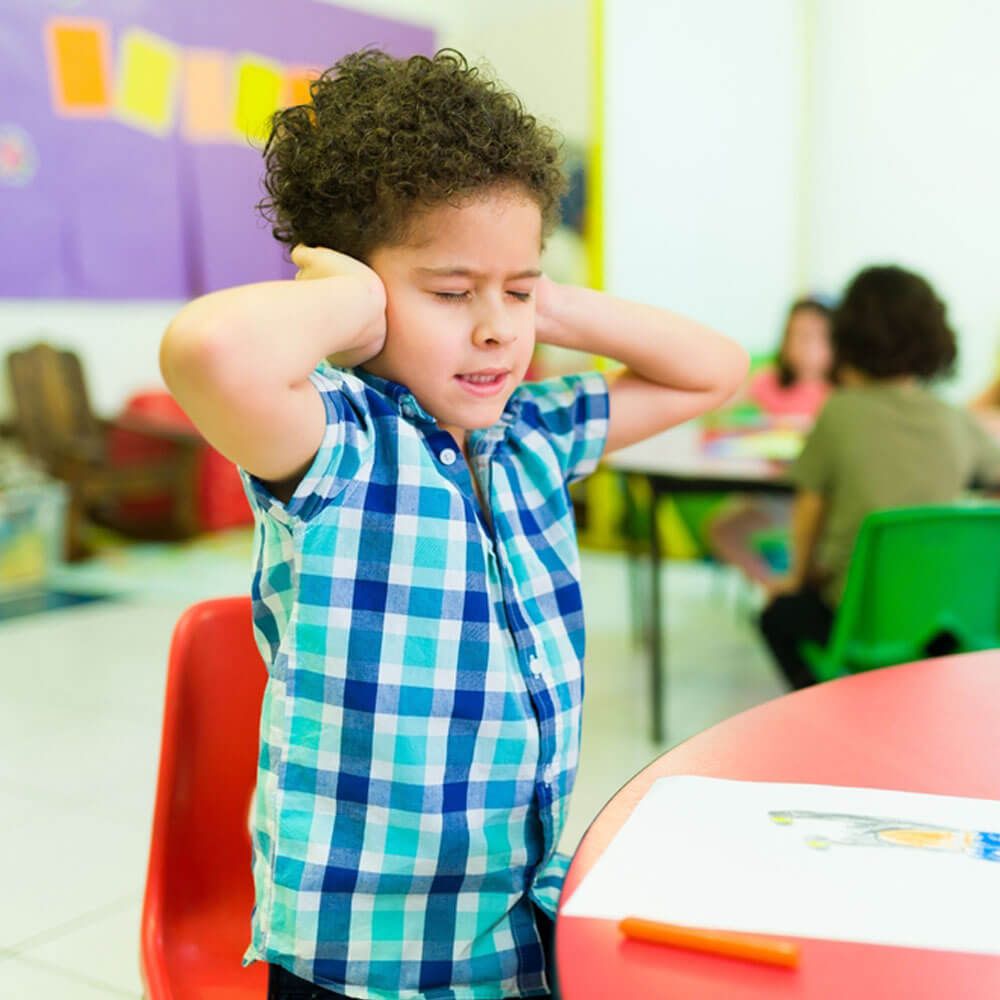
- Sensory Sensitivities: Many individuals with low functioning autism experience heightened sensitivity to sensory stimuli such as light, sound, touch, taste, or smell. They may become overwhelmed or distressed by certain sensations, leading to meltdowns or avoidance behaviors.
- Difficulty with Transitions: Changes in routine or environment can be particularly challenging for individuals with low functioning autism. They may struggle to adapt to new situations or transitions, leading to anxiety or distress.
- Delay in Developmental Milestones: Individuals with low functioning autism may exhibit delays or limitations in various areas of development, including speech and language, motor skills, and self-care abilities. These delays may be noticeable early in childhood and may require ongoing intervention and support.
Understanding the Autism Spectrum
It’s important to recognize that autism exists on a spectrum, with a wide range of abilities and support needs. While HFA and LFA represent two ends of this spectrum, there is a broad diversity of experiences and challenges within each category. By understanding and acknowledging, high functioning autism vs low functioning autism, we can better support individuals with autism in reaching their full potential and leading fulfilling lives.
High Functioning Autism (HFA)
High functioning autism refers to individuals on the autism spectrum who demonstrate relatively mild symptoms and may have average or above-average intelligence. Here’s a closer look at some key characteristics of HFA:
- Average to Above-Average Intelligence: Individuals with HFA often possess average to above-average intelligence levels. They may excel in certain academic subjects or have a keen interest and expertise in specific areas.
- Better Communication Skills: Compared to those with autism low functioning, individuals with HFA typically exhibit better communication abilities. They may have a larger vocabulary, a more nuanced understanding of language, and the ability to engage in meaningful conversations.
- Independence in Daily Living: While they may still face challenges in social interaction and behavior regulation, individuals with HFA generally require less support in activities of daily living. They can often manage tasks such as self-care, organizing their schedules, and navigating familiar environments independently.
- Narrow Range of Interests: Like many individuals on the autism spectrum, those with HFA may have intense interests in specific topics or activities. They may spend significant time researching, discussing, or engaging in these interests.
Low Functioning Autism (LFA)
Low functioning autism refers to individuals on the autism spectrum who have more severe symptoms and challenges in various areas of functioning. Here are some distinguishing features of LFA:
- Intellectual Disabilities: Unlike individuals with HFA, those with LFA may have intellectual disabilities, ranging from mild to severe. This can impact their ability to learn, understand complex concepts, and independently navigate daily tasks.
- Significant Communication Challenges: Individuals with LFA often struggle with communication skills, including both verbal and non-verbal forms. They may have limited speech, difficulty understanding language, and challenges expressing their needs and emotions.
- High Dependence on Support: LFA individuals typically require constant support and supervision to meet their daily needs. They may rely on caregivers or professionals for assistance with tasks such as personal hygiene, meal preparation, and transportation.
- Heightened Sensory Sensitivities: Sensory sensitivities are commonly more pronounced in individuals with LFA. They may be highly sensitive to sensory stimuli such as noise, light, textures, and smells, which can cause distress or agitation.
Providing Autism Support and Understanding
If you’re supporting someone with low functioning autism, here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Individualized Approach: Recognizing the uniqueness of each person with autism is essential. Just as no two neurotypical individuals are exactly alike, individuals with autism have their own set of strengths, challenges, and preferences. When providing support, it’s crucial to take into account their individual needs and tailor strategies accordingly. What works well for one person may not necessarily be effective for another.
- Communication Tools: Communication can be a significant challenge for individuals with low functioning autism. Exploring alternative communication methods can be immensely beneficial in facilitating understanding and expression. This may include using picture cards, communication boards, sign language, or assistive technology devices such as tablets with communication apps. By providing alternative means of communication, individuals with LFA can better express their thoughts, needs, and desires.
- Structured Environment: Creating a structured environment is key to helping individuals with low functioning autism feel safe, secure, and in control. Establishing routines and providing clear expectations can help reduce anxiety and improve predictability. Consistency in daily schedules, transitions, and activities can provide a sense of stability and comfort. Visual schedules or timetables can also aid in understanding what will happen next, reducing uncertainty and stress.
- Sensory-Friendly Spaces: Sensory sensitivities are common among individuals with low functioning autism. Creating sensory-friendly environments can help minimize discomfort and sensory overload. This may involve adjusting the lighting, temperature, and noise levels in the environment. Providing sensory tools such as weighted blankets, noise-canceling headphones, or fidget toys can also offer comfort and regulation. Designating quiet areas or sensory rooms where individuals can retreat when feeling overwhelmed can be immensely beneficial.
- Empathy and Patience: Approaching interactions with empathy and patience is fundamental when supporting individuals with low functioning autism. It’s important to understand that processing information and expressing thoughts or emotions may take longer for individuals with LFA. Practice active listening, validate their feelings, and be patient when waiting for responses. Avoid rushing or pressuring them, and instead, allow them the time and space they need to communicate and participate at their own pace.
Take the first step towards navigating the challenges of low-functioning autism and finding ways to thrive by reaching out for support today.
Utilizing Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) for low-functioning autism offers a structured and evidence-based approach to address symptoms and improve daily functioning. If you’re considering ABA therapy for low-functioning autism and seeking support for yourself or your child, therapy can provide valuable guidance and resources. Here’s how to get started:
- Schedule a Consultation: Reach out to Uncover Mental Health Counseling to start a conversation about ABA therapy for low-functioning autism. Our compassionate therapists offer a safe and supportive space where you can explore your options and concerns.
- Connect with a NYC Autism Therapist: Our team includes experienced therapists who specialize in ABA therapy and autism treatment. We’ll match you or your child with a therapist who can offer personalized support tailored to your unique needs and goals.
- Begin Your Autism Therapy Journey: Together with your therapist, you’ll explore the principles of ABA and how they can be applied to manage symptoms of low-functioning autism. Through structured interventions, behavior modification techniques, and skill-building exercises, therapy can empower you or your child to develop strategies for communication, social interaction, and daily living skills, enhancing overall functioning and quality of life.