Life’s a rollercoaster, and stress is the unexpected twist and turns. But here’s the secret: stress isn’t your enemy; it’s a natural response. In this blog, we’ll uncover the science of stress, how it affects your body and mind, particularly the effect of stress in the body. More importantly, we’ll explore practical strategies to conquer the impact of stress.
The Stress Response: A Survival Mechanism
Picture this: you’re a primitive human, living thousands of years ago, and you stumble upon a menacing creature in the wild. Your heart races, your muscles tense, and your senses sharpen. This is the ‘fight or flight’ response in action. Your body is gearing up to deal with a life-threatening situation, and it’s all thanks to the stress response.
Back then, this response was a crucial survival mechanism. It enabled our ancestors to make quick decisions and take immediate action when faced with imminent danger. This could mean the difference between life and death. So, stress was a biological superpower that kept our ancestors safe.
The Modern World and Ancient Responses
Fast forward to today, and our lives couldn’t be more different from those of our ancient predecessors. We’re not typically faced with life-or-death situations on a daily basis. Yet, here’s the catch: our bodies haven’t quite caught up with our fast-paced, modern lives.
When you encounter a stressful situation in the 21st century, whether it’s a looming deadline, a demanding boss, or a traffic jam, the effects of stress in the body respond in much the same way as it would to a primal threat. It’s like using a high-powered sports car for a grocery run—it’s overkill.
The Chemistry of Stress Hormones
So, what’s happening behind the scenes when stress knocks on your door? It all comes down to stress hormones, primarily adrenaline and cortisol.
- Adrenaline: Think of adrenaline as the spark plug that ignites the stress response. It’s responsible for that immediate surge of energy and heightened alertness. You might feel your heart racing, your breath quickening, and your muscles tensing as adrenaline courses through your body. It readies you for action, whether you’re preparing to fight off a predator or give a high-stakes presentation.
- Cortisol: Cortisol is the “long-term stress hormone.” It doesn’t give you the quick burst of energy like adrenaline but plays a crucial role in maintaining the stress response. Cortisol keeps you on high alert, helping you stay focused and vigilant during extended periods of stress. Stress causes chest pain too.
While these hormones were crucial for our ancestors’ survival, in the modern world, this chronic activation of the stress response can have adverse effects on our health and well-being. The very system designed to keep us safe in the face of danger can now become a source of harm if not managed effectively, highlighting the effect of stress in the body.
Physical Effects of Stress
There’s a myriad of ways the effects of stress physically affect your body. It’s like a domino effect where one symptom can trigger another, creating a chain reaction in your body.
The Heart: The Stressful Symphony
When stress barges into your life, your heart is often the first to know. Stress hormones, particularly adrenaline, act as the conductors of a high-intensity symphony within your body. They signal your heart to beat faster and more forcefully, as if it’s preparing for a sprint to safety. Your blood vessels constrict, ensuring that blood is efficiently routed to the areas that need it most during this perceived crisis.
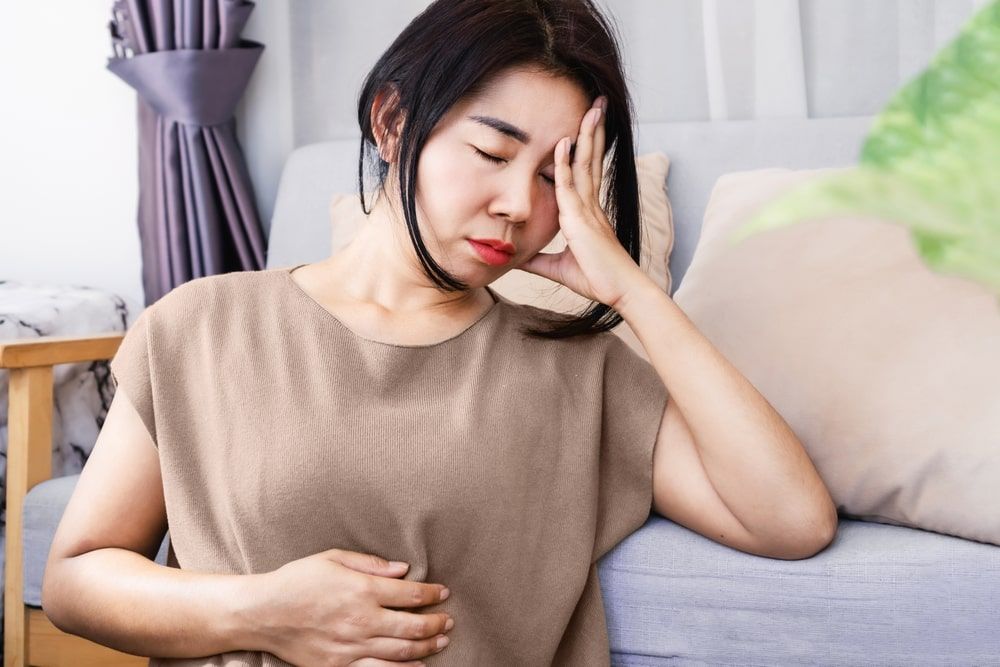
Imagine the heart as the engine of your body. It’s vital for delivering oxygen and nutrients to every nook and cranny. In response to stress, your heart starts working in overdrive, pushing blood at a rapid pace. This immediate response can lead to a temporary increase in blood pressure, which can be beneficial when a quick burst of energy is needed. But in the long run, it can place excessive strain on your heart, much like driving your car at maximum speed all the time. While stress causes chest pain, the effects of stress physically damage you in other areas as well. Over time, this elevated blood pressure can lead to cardiovascular issues, increasing the risk of heart-related problems. So, chronic stress can quite literally put a heavy burden on your heart.
The Respiratory System: The Rapid Symphony
Your respiratory system, the maestro of your breath, is also a key player in the stress symphony. When stress takes the stage, your body readies itself for action, and rapid breathing is one of the star performances.
The rapid, shallow breaths you take when stressed are your body’s way of flooding your bloodstream with extra oxygen. This is a response that served our ancestors well when facing predators or dangerous situations. However, in our modern lives, chronic stress can lead to ongoing rapid breathing. This can be uncomfortable and even trigger panic attacks for some individuals. The effects of stress physically cause respiratory issues but in this way can cause mental distress too.
Over time, this continuous rapid breathing might contribute to respiratory issues. Your body was designed to deal with brief, intense moments of stress, not prolonged periods of it. Soon enough, stress causes chest pain and the effects of stress in the body become detrimental. Chronic stress can strain your respiratory system, potentially exacerbating conditions like asthma and making it harder to catch your breath when you need to.
Digestive Troubles: The Upset Stomach
Stress and your digestive system have a complex relationship, and it’s not a harmonious one. Have you ever experienced “butterflies in your stomach” before a big presentation or important event? That sensation is the result of stress hormones getting in the way of your digestive system’s normal functioning.
When stress hormones are released, they interfere with the intricate choreography of your digestive processes. Your stomach may become more sensitive and prone to irritation, which can lead to stomach aches and cramps. The disruption can extend down the gastrointestinal highway, potentially contributing to issues like diarrhea or constipation.
In some cases, the effect of stress in the body can even play a role in the development or exacerbation of conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), where the gut becomes hypersensitive to stress-related triggers. So, it’s not just a metaphor; your gut health is indeed intricately connected to your stress levels.
Immune System: The Overwhelmed Shield
Stress isn’t just a mental and emotional battle; it’s a challenge your immune system has to face, too. When you’re under chronic stress, your body diverts resources away from less critical functions, such as your immune response, to address the immediate ‘threat’ posed by stress.
Your immune system has an intricate network of defenses, but it can become overwhelmed and less effective under constant stress. The effect of stress in the body makes you more susceptible to infections and illnesses, as your body’s ability to ward off intruders is compromised.
So, yes, the mind-body connection is indeed real. Managing stress isn’t just about feeling better mentally; it’s about keeping your body’s defense mechanism strong and resilient, especially in a world where health is a top priority.
Muscles: The Tension Tango
Imagine stress as a dance partner that you never wanted, but it insists on taking the lead. When stress takes the lead in the ‘tension tango,’ your muscles are the ones that bear the brunt of the force.
The physical tension you feel during stressful moments is your body preparing for a physical confrontation, even if the stressor is purely mental or emotional. Muscles tighten and contract as part of the fight or flight response. Over time, this chronic muscle tension, an effect of stress in the body, can take a significant toll on your musculoskeletal system.
The consequences can range from tension headaches to persistent back pain and, in extreme cases, muscular injuries. It’s as if your body is gripping the stress, refusing to let go, and, in doing so, it leaves you feeling physically drained and sore.
Sleep Disruptions: The Sleepless Interlude
Stress is a maestro in orchestrating a sleepless interlude in your life. It has a knack for hijacking your thoughts when you should be winding down, creating a never-ending loop of racing, intrusive ideas.
The result? Insomnia—the unwelcome guest who refuses to leave. Sleep is your body’s vital restoration period, but when stress disrupts your slumber, it can have far-reaching consequences. Your body and mind don’t get the chance to recuperate and recharge. This, in turn, exacerbates stress, creating a vicious cycle.
Quality sleep is crucial for both mental and physical well-being. So, when stress disrupts your slumber, it’s not just a minor inconvenience; the effect of stress in the body can severely harm your overall health and vitality.
The Brain and Stress
Your brain is the ultimate control center of your stress experience, and understanding this relationship is crucial for managing stress effectively. The effect of stress in the body includes the brain and consequent mental and emotional distress.
When stress comes knocking, your brain takes the lead role in orchestrating your body’s response. It’s a complex and highly coordinated dance that unfolds within the confines of your skull.
At the center of this dance is the amygdala, your brain’s emotional control center. This almond-shaped structure deep within your brain is responsible for processing emotions, especially fear and anxiety. When you encounter a stressful situation, the amygdala goes into overdrive. It’s like the security alarm going off when there’s a perceived threat. The amygdala signals the release of stress hormones, like adrenaline and cortisol, and sends your body into high alert mode.
On the flip side, your prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for rational thinking and decision-making, takes a backseat during the stress response. This part of your brain is essential for evaluating the situation logically and making reasoned choices. However, in the heat of a stressful moment, the amygdala’s response often drowns out the prefrontal cortex’s more measured voice. This is why, when you’re stressed, you might not always make the best choices or decisions. Stress hijacks your ability to think clearly and logically.
The Brain’s Physical Response to Chronic Stress
Now, here’s where it gets even more intriguing. Chronic stress, the kind that lingers in your life like an unwelcome guest, can physically alter the structure of your brain. One of the areas most affected is the hippocampus, a seahorse-shaped structure nestled deep within your brain. The hippocampus plays a crucial role in memory, emotion regulation, and stress response modulation.
Chronic stress can lead to a reduction in the size of the hippocampus. It’s as if the stress is slowly chipping away at this vital region. This shrinkage can have significant consequences. A smaller hippocampus means impaired memory and difficulty in regulating emotions. It can make it harder for you to manage stress effectively, creating a vicious cycle. This physical change in the brain is one of the reasons why chronic stress is often linked to mental health issues like anxiety and depression.
Moreover, when your hippocampus is compromised, your brain is more prone to respond excessively to stress, leading to heightened anxiety and an increased risk of depression. It’s like a car with a damaged brake system; it struggles to slow down and stop in response to stressors.
Coping with Stress
While stress is a natural part of life, how you deal with it can significantly impact your overall well-being and resilience.
Deep Breathing: The Power of Mindful Respiration
Deep breathing is like a reset button for your stress response. It’s a simple yet powerful technique to calm your body and mind when stress begins to surge. When you consciously engage in deep, mindful breathing, you activate your body’s relaxation response. The effect of stress in the body can improve with deep breathing and relaxation techniques. Deep breathing is a portable stress relief tool you can use anywhere, anytime. It’s like hitting the pause button on stress and allows you to regain control over your reactions. Here’s how it works:
- Find a Quiet Space: Step away from the source of stress, if possible, to a quiet and peaceful place.
- Take a Seat or Lie Down: Sit in a comfortable position or lie down on your back.
- Inhale Slowly: Breathe in deeply through your nose for a count of four, allowing your abdomen to rise.
- Exhale Gradually: Exhale slowly through your mouth for a count of four, focusing on the sensation of your breath leaving your body.
- Repeat: Continue this pattern for a few minutes or until you feel a sense of calm washing over you.
Exercise: The Stress-Busting Workout
Physical activity is a formidable ally in the battle against stress. Regular exercise not only keeps you physically fit but also helps manage stress effectively. It’s not about running a marathon; even a brisk walk, yoga, or a dance class can be beneficial. The key is to find an activity you enjoy and make it a part of your routine. Here’s how it works:
- Release of Endorphins: Exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, your body’s natural mood lifters. These chemicals are like a dose of positivity, countering the effects of stress hormones.
- Stress Hormone Reduction: Physical activity reduces the production of stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol, which can help your body return to a calmer state more quickly.
- Improved Sleep: Regular exercise promotes better sleep quality, which is essential for your body to recover from the wear and tear of daily stress.
Sleep: The Ultimate Stress Recovery
Sleep is your body’s natural recovery mechanism. When you sleep well, you give your body and mind the opportunity to repair and recharge. Quality sleep not only helps you manage stress more effectively but also supports overall health and well-being. Here’s how you can prioritize quality sleep:
- Establish a Routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same times each day, even on weekends. Consistency helps regulate your body’s internal clock.
- Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Ensure your bedroom is comfortable, dark, and cool. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows.
- Limit Screen Time: Avoid screens (phones, tablets, TVs) at least an hour before bedtime. The blue light emitted from screens can interfere with your sleep cycle.
- Relaxation Practices: Engage in calming activities before bedtime, such as reading, meditation, or deep breathing.
Social Connections: The Human Support System
Human connection is a powerful antidote to stress. Talking to friends and family provides emotional support and a sense of belonging. Remember, you don’t have to face stress alone. Reach out and lean on your social support system when needed. Here’s how you can harness the power of social connections:
- Share Your Feelings: Don’t be afraid to open up and share your worries and fears with someone you trust. Sometimes, just talking about what’s bothering you can be incredibly relieving.
- Seek Perspective: Friends and family can offer different perspectives on your stressors, helping you see them in a new light.
- Offer Support: Building strong social connections goes both ways. Supporting others during their stressful times can be equally rewarding.
Mindfulness and Meditation: The Art of Being Present
Mindfulness and meditation practices are like a sanctuary for your mind. They help you stay grounded and focused in the present moment, reducing stress and anxiety. Here’s how they work:
- Practice Regularly: Set aside time each day for mindfulness or meditation. Even just a few minutes can make a difference.
- Breathe and Observe: Focus on your breath or a specific aspect of the present moment. When your mind wanders, gently bring your attention back to your chosen focus.
- Non-Judgmental Awareness: Accept your thoughts and feelings without judgment. It’s about observing them without trying to change them.
You don’t have to tackle the physical effects of stress alone. Our stress management counselors in NYC are here to help you regain your health and vitality while equipping you with the knowledge and resources you need to lead a stress-free, healthy life.
Navigating the impact of stress on your body can be a challenging journey, especially when you’re wondering, “How does stress affect my body?” The answer is significant! Stress can take a toll on your physical health. It’s crucial to understand these effects and find ways to manage and mitigate stress. At Uncover Mental Health Counseling, we recognize the importance of equipping you with the knowledge and tools to combat stress. Here’s how:
- Reach Out to Uncover Mental Health Counseling: Start by getting in touch with us for a complimentary consultation call. Our team is here to answer your questions and guide you through understanding the physical effects of stress on your body.
- Consult with Our Stress Management Specialists: Once you’ve taken the first step, connect with our experienced therapists who specialize in addressing the impacts of stress. In your initial session, you can explore your concerns and learn about strategies to manage stress’s effects on your body.
- Reclaim Your Health and Well-being: Embark on a journey to understand and counteract the effects of stress on your body. We’ll provide you with the support and guidance you need to improve your physical health, reduce stress-related issues, and enhance your overall well-being.